Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of supply chain management, efficiency and accuracy are paramount. One technology that has emerged as a game-changer in the warehouse industry is Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID). RFID offers a sophisticated solution to traditional barcode systems, providing real-time visibility, enhanced data accuracy, and improved operational efficiency. This article explores the multifaceted applications of RFID in warehouses, delving into its benefits, challenges, and the transformative impact it can have on modern supply chain operations.
Understanding RFID Technology
RFID technology is built on the principle of wireless communication through radio- frequency signals. It consists of three main components: RFID tags, RFID readers, and a backend system. The RFID tags, equipped with a unique identifier, can be attached to products, pallets, or containers. RFID readers, strategically placed throughout the warehouse, capture the information stored on the tags by emitting radio signals. The backend system processes and interprets this data, providing real-time insights into inventory movements and locations.
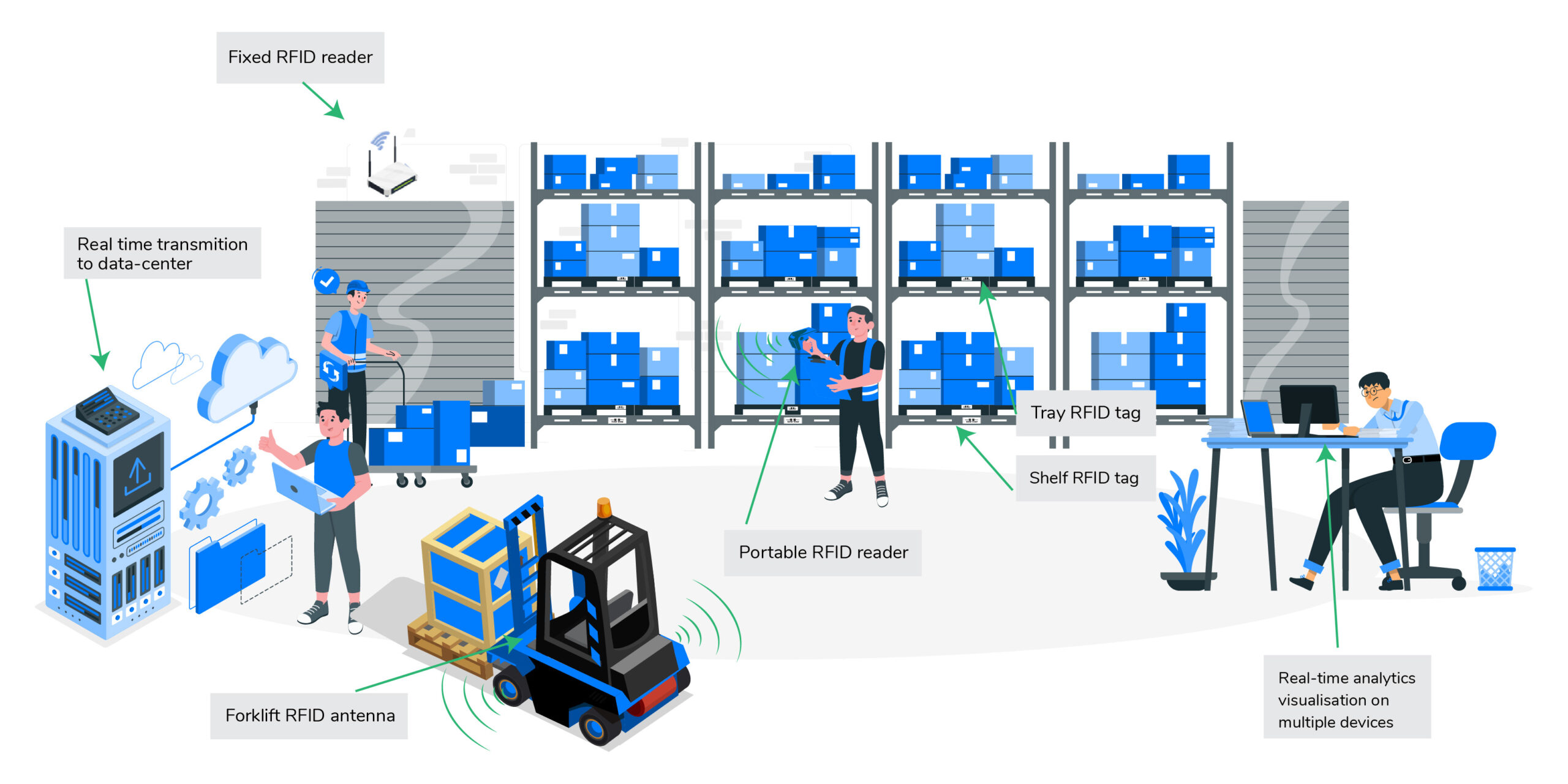
Benefits of RFID in Warehousing
Real-Time Visibility:
One of the key advantages of RFID technology is its ability to provide real-time visibility into the entire warehouse ecosystem. Traditional barcode systems require line-of-sight scanning, making it time-consuming and prone to errors. RFID, on the other hand, enables simultaneous scanning of multiple items without direct line-of- sight, significantly reducing the time spent on inventory checks and increasing overall accuracy.
Improved Inventory Accuracy:
RFID technology eliminates the need for manual data entry and reduces the risk of human errors associated with traditional methods. With RFID, each item in the warehouse is uniquely tagged, allowing for precise tracking and automatic updates in the inventory management system. This leads to improved accuracy in stock levels, reducing instances of stockouts or overstocking.
Streamlined Operations:
RFID accelerates various warehouse processes, from receiving and picking to packing and shipping. Automated data capture ensures that the right products are picked, packed, and shipped, minimizing order fulfillment errors. This streamlining of operations not only increases efficiency but also enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring timely and accurate deliveries.
Enhanced Security:
RFID technology enhances warehouse security by providing real-time alerts for unauthorized movements or potential theft. If an item with an RFID tag is moved without proper authorization, the system triggers an alarm, allowing quick response and mitigation of security threats.
Efficient Asset Management:
Beyond inventory control, RFID can be used for managing warehouse assets such as forklifts, pallets, and equipment. By attaching RFID tags to these assets, warehouse managers can monitor their location, usage, and maintenance needs in real time, optimizing resource allocation and extending the lifespan of valuable equipment.
Challenges and Considerations
While RFID presents numerous advantages, its implementation comes with challenges that need to be carefully addressed:
Initial Investment:
The upfront cost of implementing RFID technology can be a significant barrier for some warehouse operators. However, it’s essential to consider the long-term benefits and return on investment (ROI) in terms of improved efficiency, reduced errors, and enhanced overall productivity.
Integration with Existing Systems:
Integrating RFID technology with existing warehouse management systems (WMS) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems can be complex. Warehouse operators need to invest in compatible software and ensure seamless integration to harness the full potential of RFID.
Training and Change Management:
Implementing RFID requires training the warehouse staff to adapt to the new technology and processes. Resistance to change is common, and effective change management strategies are essential to ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits of RFID.
Standardization:
The lack of universal standards for RFID technology can pose challenges, particularly in a global supply chain where different regions may have varying regulations and frequencies for RFID. Standardization efforts are ongoing, but industry stakeholders must collaborate to establish common protocols.
Applications of RFID in Warehousing
Inventory Management:
RFID technology revolutionizes inventory management by providing real-time visibility into stock levels, locations, and movements. This leads to improved accuracy in stock counts, reduces the risk of stockouts or overstocking, and streamlines the entire inventory replenishment process.
Order Fulfillment and Picking:
RFID accelerates the order fulfillment process by automating data capture during picking and packing. Warehouse staff equipped with RFID readers can quickly locate and verify the correct items, minimizing errors and increasing the speed of order processing.
Shipping and Receiving:
RFID enhances the efficiency of shipping and receiving operations. RFID tags on incoming shipments enable automatic data capture, updating the inventory system in real time. This not only expedites the receiving process but also ensures accurate tracking of goods entering and leaving the warehouse.
Asset Tracking:
RFID is a powerful tool for tracking and managing warehouse assets, including equipment, vehicles, and containers. By attaching RFID tags to these assets, warehouse managers can monitor their location, usage, and maintenance needs, optimizing resource allocation and reducing downtime.
Work-in-Progress Tracking:
In manufacturing warehouses, RFID technology can be used to track the progress of products through various stages of production. This real-time visibility enables better production planning, quality control, and timely identification of bottlenecks in the manufacturing process.
Cold Chain Management:
For warehouses dealing with temperature-sensitive goods, such as pharmaceuticals or perishable food items, RFID plays a crucial role in ensuring the integrity of the cold chain. RFID tags equipped with temperature sensors can monitor and record temperature data throughout the entire supply chain, helping prevent spoilage and maintain product quality.
TagMatiks Wedge offers a range of features and benefits that make it a powerful tool for RFID data collection. Here’s a breakdown of the key advantages:
Simple Data Collection:
Utilize the in-built Inventory function for quick RFID tag counts associated with your items.
Toggle the power on the RFID handheld to control the read range, providing flexibility in data collection.
Integration and Connectivity:
Configure fields for export and customize header information to meet your specific needs.
Export collected data seamlessly using various options such as APIs and File Generation (CSV and Text).
Robust Device Support:
TagMatiks Wedge supports a wide variety of RFID readers and handhelds out of the box.
Stay updated with the latest list of supported devices by contacting the TagMatiks team.
Extremely Configurable:
Choose specific fields and memory banks of RFID tags for collection and reporting. Name and configure inventories for easy reference, and apply data filters to obtain precise information.
Low Cost:
TagMatiks Wedge is available as a cost-effective, one-time license per RFID handheld or sled, offering affordability.
Tag Validation:
Ensure proper encoding of RFID tags, including compliance with GS1 standards and customizable options for validation.
Simple yet Powerful:
Features like Find Item enable pinpointing of assets and items using RFID handhelds or sleds.
Collect additional metadata such as GPS coordinates (latitude/longitude) during the counting process.
Reference File:
Import reference files to incorporate application-specific information and tailor the view to suit your unique use case.
TM_Wedge_Handhelds:
TagMatiks Wedge seamlessly integrates with RFID handhelds, allowing for the rapid scanning of hundreds of tags per second.
Automate business processes efficiently using RFID technology.
In summary, TagMatiks Wedge provides a user-friendly yet powerful solution for RFID data collection, offering flexibility, configurability, and cost-effectiveness.
Conclusion
The integration of RFID technology in warehouse management marks a paradigm shift in the way supply chains operate. The benefits of real-time visibility, improved accuracy, and streamlined operations position RFID as a cornerstone for modern warehouse efficiency. While challenges such as initial investment and integration complexities exist, the long-term gains in productivity and customer satisfaction make RFID a worthwhile investment for forward-thinking warehouse operators. As the technology continues to evolve and standards become more widespread, RFID will likely become an indispensable tool for optimizing supply chain processes and ensuring the success of warehouses in an increasingly competitive market.
