Using RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) portals for shipment verification in warehouses revolutionizes the efficiency and accuracy of the process. This technology streamlines asset tracking, enhances security, and reduces errors. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of RFID portals, exploring their functionality, benefits, implementation strategies, and future prospects in the realm of warehouse logistics.

Understanding RFID Portals:
RFID portals are strategic entry and exit points equipped with RFID readers and antennas. These devices communicate wirelessly with RFID tags attached to items or pallets. Each tag contains unique identifiers that can be read by the portals, allowing for seamless tracking and monitoring of goods throughout the supply chain.
Role of RFID Tags:
RFID Tags are the key component of shipment verification systems relying on RFID technology. These small electronic devices, typically attached to items or pallets, contain unique identifiers that can be wirelessly read by RFID readers. Unlike traditional barcodes, RFID tags do not require line-of-sight scanning, enabling rapid and automated data capture.
RFID Readers and Antennas:
RFID portals are strategically positioned entry and exit points within the warehouse, equipped with RFID readers and antennas. As shipments pass through these portals, RFID readers emit radio waves, which are then captured by the antennas and used to communicate with the RFID tags. This seamless interaction allows for the automatic identification and tracking of goods in real-time.
RFID Software:
The functionality of RFID portals is further enhanced by RFID software, which manages the data collected from RFID readers and RFID tags. This software plays a crucial role in processing, analyzing, and interpreting RFID data, providing warehouse managers with actionable insights into inventory movements.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) portals are an efficient technology for automating shipment verification in warehouses.
Here's how RFID Portals Can Be Deployed
1. Infrastructure Setup:
Implementing RFID portals requires careful planning and infrastructure setup. This includes installing RFID readers and antennas at strategic locations within the warehouse, as well as integrating them with existing inventory management systems.
2. Tagging Items:
The process begins with tagging each item or pallet with TagMatiks RFID tags. These tags contain unique identifiers that can be read by RFID readers. Integration with Existing Systems: RFID portals should be seamlessly integrated with existing warehouse management systems (WMS) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. This integration enables the automatic transfer of data between systems, eliminating the need for manual data entry and reconciliation.
3. Incoming Shipment Verification:
As shipments arrive at the warehouse, RFID portals placed at entry points automatically scan the RFID tags on the incoming items. The RFID readers capture the unique identifiers of the RFID tags, which are then matched against the expected shipment data in the warehouse management system (WMS).
Any discrepancies between the received items and the expected shipment can be immediately flagged for further investigation.
4. Inventory Tracking:
Once the items are verified and accepted into the warehouse, RFID portals throughout the facility continuously monitor the movement of items in real time.
As items are moved within the warehouse, RFID readers at different checkpoints update the inventory records automatically without manual intervention.
This ensures accurate inventory management and reduces the likelihood of stockouts or overstock situations.
Inventor Tracking is a critical aspect of warehouse operations, and RFID portals play a key role in ensuring accuracy and efficiency in this area. Here’s a more detailed explanation of how RFID portals are used for inventor Tracking:
Overall, RFID portals enable warehouses to achieve greater accuracy, efficiency, and visibility in inventory management, leading to reduced costs, improved customer service, and enhanced operational performance.
5. Order Fulfillment
When an order is received, RFID portals play a crucial role in the picking and packing processes.
As warehouse workers pick items for an order, RFID readers at packing stations verify that the correct items are being packed by scanning the RFID tags. Any errors, such as picking the wrong item or quantity, can be immediately identified and corrected before shipping.
6. Shipment Verification:
- Before items are shipped out of the warehouse, they pass through RFID portals at the outbound dock.
- The RFID readers scan the tags on the items to verify that the correct items are being loaded onto the outgoing trucks.
- This final verification step ensures that the right items are sent to the right destinations, reducing shipping errors and customer dissatisfaction.
7. Data Integration and Reporting:
- Throughout these processes, data collected from RFID portals is integrated with the warehouse management system.
- Managers can access real-time information about inventory levels, shipment statuses, and any discrepancies through customizable reports and dashboards.
- This data visibility enables better decision-making and helps in optimizing warehouse operations.
8. Employee Training:
Warehouse staff must be adequately trained on the use of RFID portals and associated technologies. This includes understanding how to troubleshoot common issues, interpret data generated by the system, and leveraging RFID technology to improve workflow efficiency.
9. Continuous Optimization:
Implementing RFID portals is not a one-time effort; it requires continuous optimization and fine-tuning. Regular maintenance, software updates, and performance monitoring are essential to ensure the long-term effectiveness of the system.
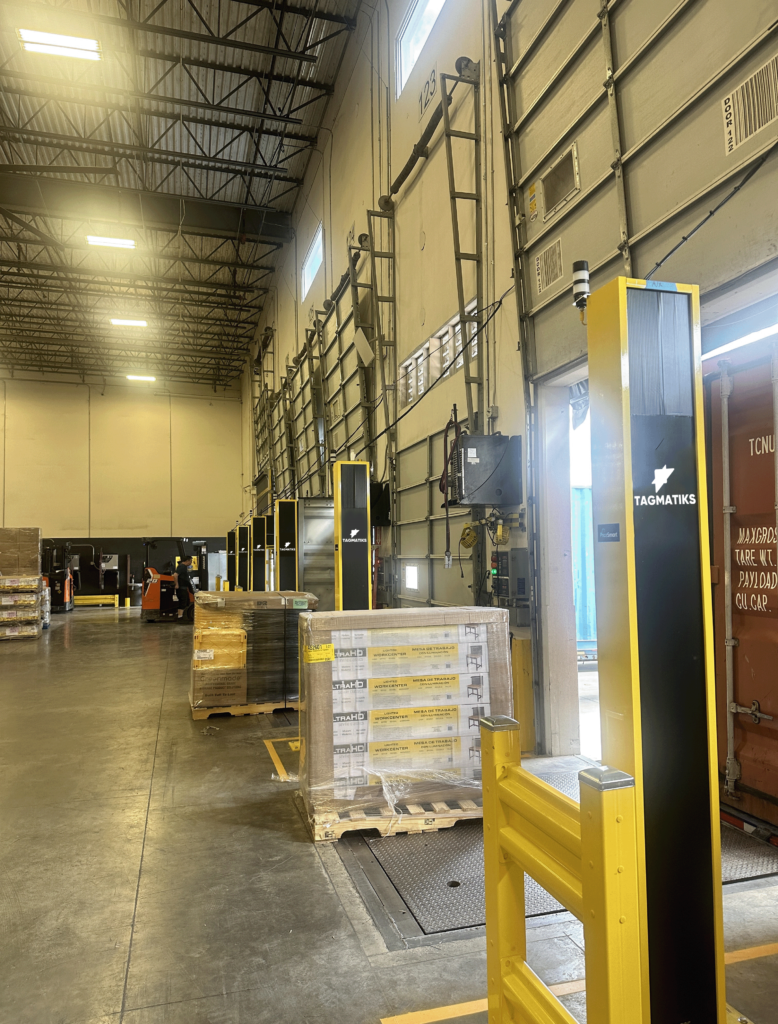

Benefits of RFID Portals for Shipment Verification:
Real-Time Visibility:
RFID portals provide real-time visibility into inventory movements. As shipments pass through these portals, data is instantly captured, enabling warehouse managers to monitor the location and status of goods at all times.
Automation:
Manual shipment verification processes are time-consuming and prone to errors. RFID portals automate this task by automatically reading and recording tag data as shipments enter or leave the warehouse. This automation reduces labor costs and improves accuracy.
Enhanced Security:
With RFID portals, warehouses can implement robust security measures. Unauthorized items can be flagged as they pass through the portals, reducing the risk of theft or tampering.
Improved Efficiency:
Traditional methods of shipment verification involve scanning individual barcodes or serial numbers. RFID portals streamline this process, allowing for the simultaneous scanning of multiple items as they pass through the portal, significantly improving efficiency.
Data Analytics:
The data collected by RFID portals can be analyzed to identify trends, optimize inventory levels, and improve overall warehouse operations. Insights gained from this data can drive informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Tagging Strategy:
Each item or pallet in the warehouse must be equipped with an RFID tag. Choosing the right tagging strategy, including tag placement and type, is crucial to ensure optimal read rates and performance.
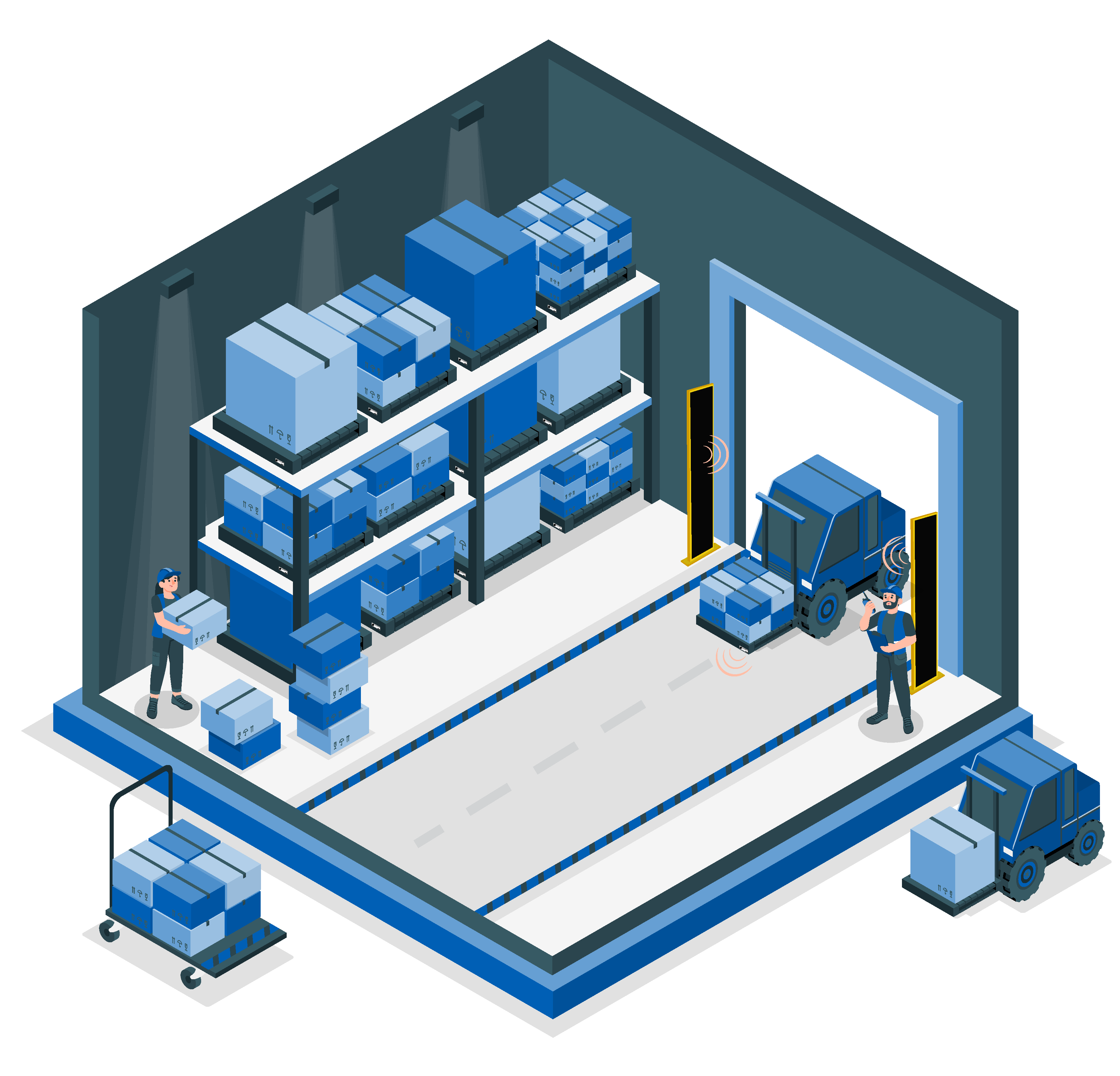
Future Prospects of portals for shipment verification in warehouses revolutionize
The future of RFID portals in warehouse logistics looks promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and increasing adoption across industries. Some emerging trends and developments include:
IoT Integration:
RFID portals are increasingly being integrated with other Internet of Things (IoT) devices, such as sensors and cameras, to provide a more comprehensive view of warehouse operations.
Artificial Intelligence:
AI-powered analytics can extract valuable insights from the vast amounts of data generated by RFID portals, enabling predictive maintenance, demand forecasting, and optimization of supply chain processes.
Blockchain Integration:
Blockchain technology offers enhanced security and transparency in supply chain management. By integrating RFID data with blockchain networks, warehouses can create immutable records of inventory movements, reducing the risk of fraud and counterfeit goods.
Miniaturization and Cost Reduction:
Ongoing advancements in RFID technology are driving miniaturization and cost reduction of RFID tags and readers, making them more accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and enabling broader adoption across industries.
Conclusion
RFID portals offer a powerful solution for shipment verification in warehouses, providing real-time visibility, automation, enhanced security, and improved efficiency. By implementing RFID portals strategically and leveraging emerging technologies, warehouses can optimize their operations, reduce costs, and gain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic marketplace.