Introduction
In the fast-paced world of healthcare, efficient management of assets can mean the difference between life and death. With the advent of advanced technologies like RFID, hospitals have found a powerful tool to streamline their operations and enhance patient care. This article explores the benefits, challenges, and implementation of RFID asset tracking in hospitals, providing a comprehensive guide for healthcare administrators and decision-makers.
What is RFID (Radio Frequency Identification)?
RFID, or Radio Frequency Identification, is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags contain electronically stored information that can be read from a distance using RFID readers. In healthcare settings, RFID plays a crucial role in tracking medical assets, improving inventory management, and enhancing patient safety.
Importance of Asset Tracking in Hospitals
Efficient asset tracking is vital in hospitals to ensure that medical equipment and supplies are readily available when needed. It helps in optimizing workflows, reducing costs, and improving patient care outcomes. Hospitals face unique challenges in asset management, ranging from equipment loss and theft to compliance with regulatory standards. RFID technology offers a promising solution to these challenges by providing real-time visibility and accurate tracking of assets.
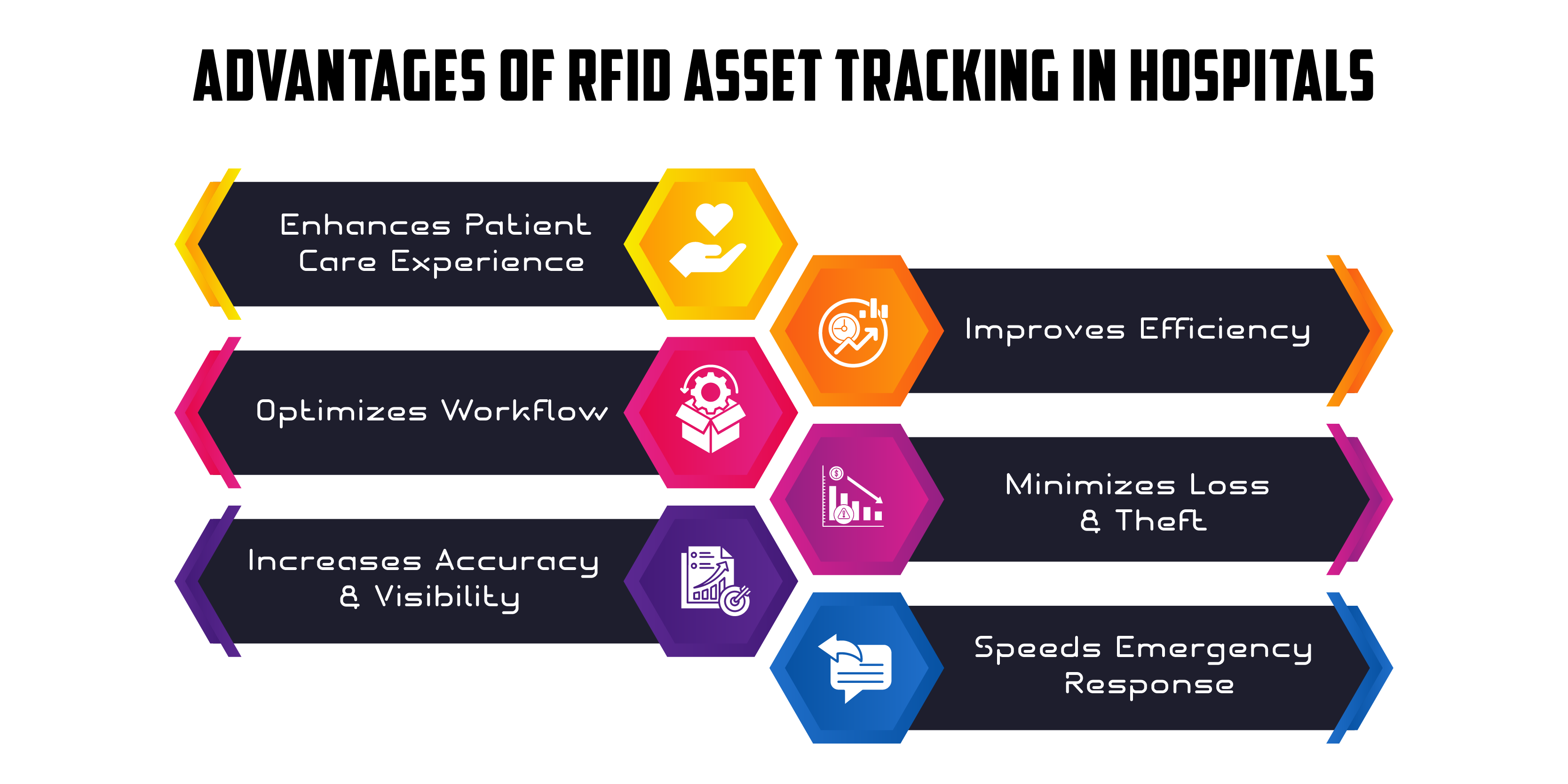
Enhancing Patient Care Through Efficient Asset Tracking
RFID asset tracking enables hospitals to efficiently manage medical equipment and supplies. By knowing the exact location of assets at any given time, healthcare providers can reduce patient waiting times and improve treatment outcomes. For example, nurses can quickly locate infusion pumps or defibrillators needed for urgent patient care, leading to faster response times and better patient outcomes.
Improving Operational Efficiency and Reducing Costs
RFID technology automates many manual processes involved in asset tracking, thereby improving operational efficiency. Hospitals can reduce labor costs associated with manual inventory counts and asset searches. For instance, instead of spending hours manually counting inventory, RFID systems can perform these tasks in minutes, allowing staff to focus on patient care.
Optimizing Staff Productivity and Workflow
With RFID, hospital staff can spend less time searching for equipment and more time on patient care. This optimization of workflow helps in reducing stress and fatigue among healthcare workers. By ensuring that the right equipment is available at the right time, RFID improves staff productivity and job satisfaction.
Reducing Loss and Theft of Medical Assets
One of the major challenges hospitals face is the loss or theft of expensive medical equipment. RFID tags can be attached to assets like wheelchairs, monitors, and surgical instruments, enabling hospitals to track their movements in real-time. This reduces the risk of theft and helps in quickly recovering misplaced items.
Enhancing Data Accuracy and Real-Time Visibility
RFID provides accurate, real-time data on asset location and status. This visibility helps hospitals maintain accurate inventory records and prevent stockouts. For example, RFID systems can automatically alert staff when inventory levels are low or when equipment needs maintenance, ensuring that patient care is not compromised.
Facilitating Rapid Emergency Response and Patient Care
In emergencies, every second counts. RFID technology allows hospitals to quickly locate and deploy critical equipment needed for emergency procedures. This rapid response can save lives and improve patient outcomes. For example, during a cardiac arrest, RFID can ensure that a defibrillator is readily available, potentially increasing the chances of survival.
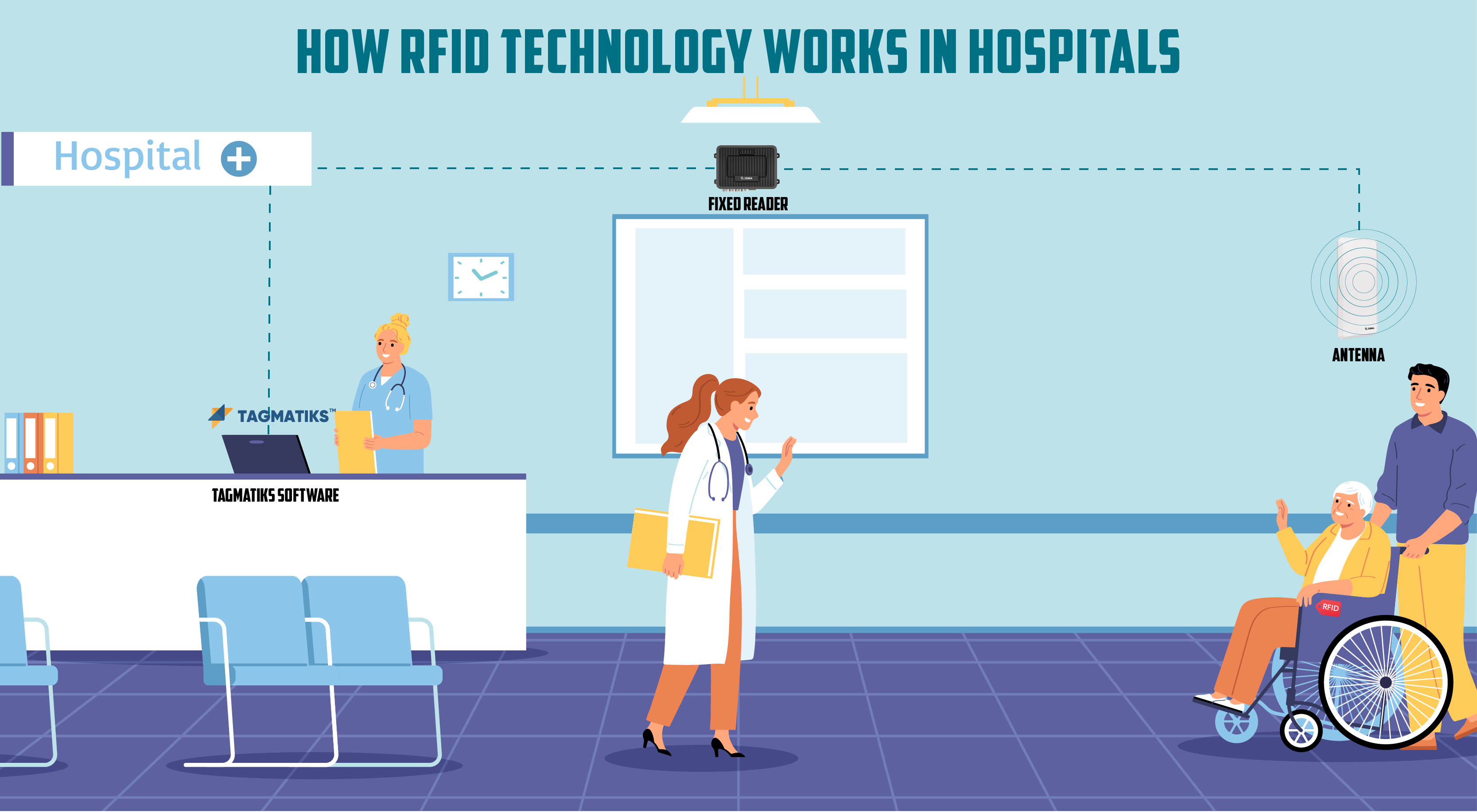
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology in hospitals uses electromagnetic fields to identify and track tags attached to medical assets. RFID systems include tags on equipment, readers to capture data, and software for integration with hospital systems. This technology enables real-time asset tracking, improves inventory management, and enhances patient care by ensuring equipment availability. RFID tags can be passive, active, or specialized for hospital use, like autoclave-resistant tags.
Types of RFID Tags Used in Hospitals
Passive RFID Tags
Passive RFID tags have no internal power source and are activated by RFID reader’s radio signals. They are commonly used for tracking medical supplies and equipment due to their low cost and durability.
Semi-Passive RFID Tags
Semi-passive RFID tags, also known as battery-assisted passive (BAP) tags, have a small battery that powers the tag’s circuitry and enables additional features such as sensors for environmental monitoring (e.g., temperature, humidity). These tags are often used for tracking temperature-sensitive medications or equipment in hospitals where environmental conditions need to be monitored closely.
Specialized RFID Tags for Medical Equipment
Specialized RFID tags are designed for specific medical applications, such as autoclave-resistant tags used for tracking sterilized equipment, temperature- sensitive tags used for tracking sensitive vaccines and medications, and butterfly- style RFID tags for discreet tracking of medical implants and devices.
Applications of RFID in Hospitals
Tracking Medical Equipment and Devices
RFID technology enables hospitals to track the location and status of medical equipment, ensuring that devices are available when needed and reducing the time spent searching for them.
Managing Inventory and Supplies
RFID automates inventory management, reducing stockouts and ensuring that hospitals have the supplies they need to deliver quality patient care.
Enhancing Patient and Staff Safety
RFID enhances patient safety by ensuring that equipment is properly maintained and sterilized. It also improves staff safety by reducing the risk of injury from moving heavy equipment.
RFID Implementation Steps for Hospitals
Planning and Assessment
Assess hospital needs and challenges, define goals for RFID implementation, and create a project plan.
Choosing the Right RFID System and Tags
Select RFID tags and RFID readers based on hospital requirements, such as asset types, environment, and budget.
Integration with Hospital Systems
Integrate RFID systems with existing hospital systems, such as electronic health records (EHR) and inventory and asset tracking software like; TagMatiks Wedge, TagMatiks Asset Tracking, and TagMatiks AT Lite, to maximize efficiency and data accuracy.
Cost Considerations: Is RFID Worth the Investment?
Consider the initial costs of RFID implementation versus potential long-term savings from improved asset management, reduced equipment loss, and enhanced operational efficiency. Calculate the return on investment (ROI) based on factors such as labor savings, reduced equipment downtime, reduced misplacement and theft of equipments, and improved patient care outcomes.
Best Practices for Implementing RFID in Hospitals
Best Practices for Implementing RFID in Hospitals involve engaging hospital staff and stakeholders to ensure buy-in and successful adoption, providing comprehensive training on RFID systems, and offering ongoing technical support to address any issues that may arise.
Conclusion
RFID4U is a leading provider of RFID training, consulting, and implementation services. With extensive experience in healthcare, RFID4U helps hospitals optimize asset management through RFID technology, improving operational efficiency and patient care.
RFID technology offers significant benefits to hospitals, including improved patient care, enhanced operational efficiency, and reduced costs. By implementing RFID asset tracking systems, hospitals can overcome current asset management challenges and prepare for the future of healthcare.
