Introduction
In today’s dynamic business landscape, the ability to effectively track assets is paramount for organizations across industries. Whether it’s managing inventory in a warehouse, tracking equipment in a healthcare facility, or monitoring tools on a construction site, the ability to accurately locate and manage assets can significantly impact operational efficiency, cost savings, and overall productivity.
Among the myriad of technologies available for asset tracking, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) stands out as a powerful solution offering real-time visibility, automated data capture, and improved accuracy. However, with a wide range of RFID tags available in the market, selecting the right one can be a daunting task. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the intricacies of RFID tags for asset tracking, exploring key considerations, technical specifications, and best practices to help you make informed decisions and maximize the efficiency of your asset-tracking system.
Understanding RFID Technology:
Before delving into the specifics of RFID tags for asset tracking, it’s essential to have a basic understanding of how RFID technology works. At its core, RFID comprises three main components: tags, readers, and a backend system.
RFID Tags:
These are small electronic devices that contain a microchip and an antenna. The microchip stores unique identifiers and other relevant data about the asset, while the antenna enables communication with RFID readers via radio waves.
RFID Readers:
Readers are devices that emit radio waves and receive signals from RFID tags. They capture data from tags within their read range and transmit it to the backend system for processing and analysis.
Backend System:
This encompasses the software and infrastructure responsible for managing and processing RFID data. It includes databases, middleware, and applications that interpret the data captured by RFID readers, enabling organizations to track, monitor, and manage their assets effectively.
Now that we have a basic understanding of RFID technology, let’s explore the key factors to consider when selecting RFID tags for asset tracking:
Read Range and Accuracy:
Read range refers to the maximum distance at which an RFID reader can communicate with a tag. For asset tracking applications, especially in large warehouses or facilities, it’s crucial to choose RFID tags with an appropriate read range to ensure reliable and accurate data capture. Factors such as tag orientation, interference from metal or liquids, and environmental conditions can impact read range and accuracy. Consider conducting site surveys and testing different tag configurations to optimize read performance in your specific environment.
Durability and Environmental Considerations:
Assets may be subjected to various environmental conditions such as moisture, extreme temperatures, or physical impact. Therefore, it’s essential to choose RFID tags that are durable enough to withstand these conditions without compromising performance.
Look for tags with rugged enclosures, specialized coatings, or encapsulation that offer protection against moisture, dust, and mechanical stress. Additionally, consider the operating temperature range and environmental certifications of the tags to ensure suitability for your application.
Size and Form Factor:
The size and form factor of RFID tags play a significant role in asset tracking, especially when tracking assets of different shapes and sizes. Smaller tags are ideal for tracking smaller items or assets with limited space for tagging, while larger tags may offer better read performance for larger assets.
Additionally, consider the mounting options available for different form factors to ensure easy installation on various asset types. Some tags come with adhesive backing, while others may require screws or zip ties for attachment.
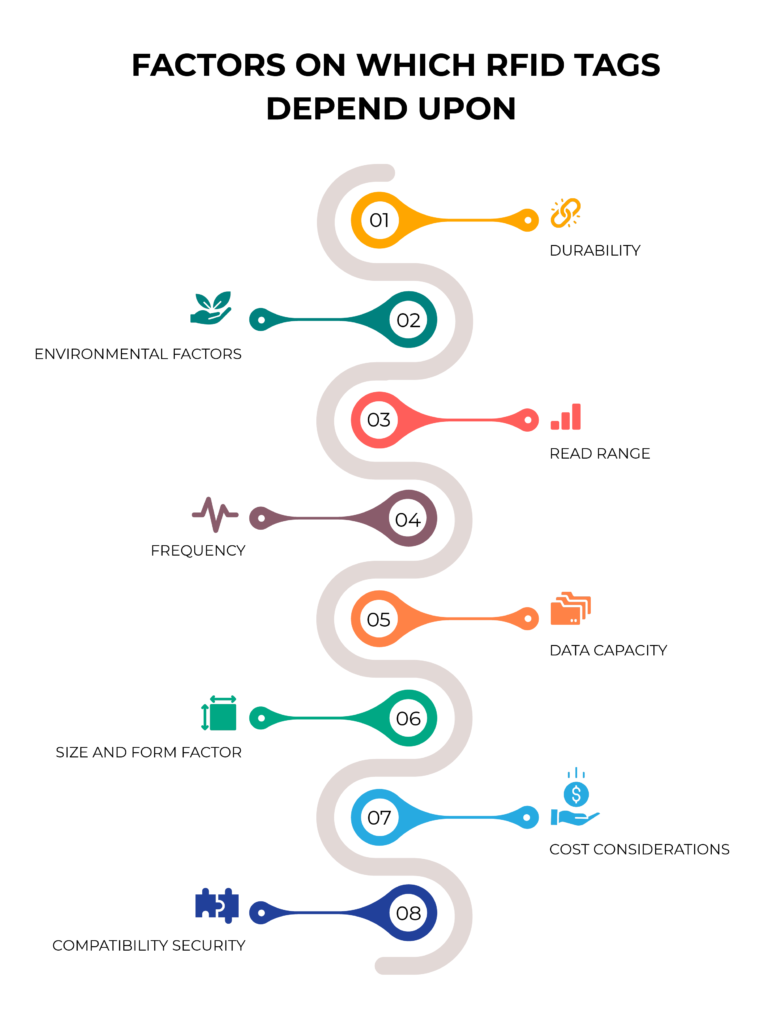
Frequency:
RFID tags operate at different frequencies, each with its advantages and limitations. Frequency is also important. (Low-frequency (LF), high-frequency (HF), and Typically ultra-high frequency (UHF)) are the most common RFID frequencies used for asset tracking.
Low-frequency tags are suitable for close-range applications and are less affected by interference from metal or liquids. High-frequency tags offer improved read performance and are commonly used for tracking assets in healthcare and retail environments. Ultra-high frequency tags provide longer read ranges and faster data transfer rates, making them ideal for asset tracking in large areas such as warehouses and manufacturing facilities.
Data Storage and Encoding:
Depending on the complexity of your asset tracking system, consider the data storage capacity and encoding capabilities of RFID tags. Some tags offer additional memory for storing asset-specific information, such as maintenance records or location history.
Ensure compatibility with your RFID software and systems for seamless integration and data management. Consider whether you require read-only or read-write capabilities for your application and choose tags accordingly.
Cost Considerations:
Cost is always an important consideration when implementing any technology solution. While RFID tags offer significant benefits for asset tracking, it’s essential to balance the cost of tags with the potential return on investment in terms of improved efficiency, accuracy, and asset visibility.
Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including tag costs, reader infrastructure, and ongoing maintenance, to determine the most cost-effective solution for your organization. Consider factors such as tag lifespan, reliability, and scalability when assessing the long-term cost implications.
Compliance and Standards:
Ensure that the RFID tags you choose comply with relevant industry standards and regulations, especially if you operate in highly regulated sectors such as healthcare, aerospace, or defense.
Compliance with standards ensures interoperability with existing systems and facilitates seamless integration into your asset-tracking ecosystem. Look for tags that meet international standards such as ISO 18000 series for RFID technology and industry-specific standards where applicable.
Conclusion:
Effective asset tracking is essential for organizations seeking to optimize operations, reduce costs, and enhance productivity. RFID technology offers a powerful solution for asset tracking, providing real-time visibility, automated data capture, and improved accuracy. By carefully considering factors such as read range, durability, frequency, data storage, cost, and compliance, organizations can select RFID tags that best suit their specific asset tracking requirements.
Whether you’re managing inventory in a warehouse, tracking equipment in a healthcare facility, or monitoring tools on a construction site, choosing the right RFID tags is crucial for maximizing the efficiency of your asset-tracking system. By leveraging the insights and best practices outlined in this comprehensive guide, organizations can unlock the full potential of RFID technology and gain a competitive edge in today’s rapidly evolving business landscape.