Introduction to RFID in Retail
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology has become a pivotal tool in modern retail operations. By leveraging radio waves to identify and track items, RFID has revolutionized inventory management, loss prevention, and customer service. This article delves into the detailed reasons behind the adoption of RFID by retailers and explores its wide-ranging impacts on the retail landscape.

The key advancements that have propelled RFID into the retail mainstream include:
Cost Reduction:
The cost of RFID tags has decreased dramatically, making it economically viable for retail applications.
Technological Advancements:
Improvements in RFID readers, RFID Software integration, and RFID tag durability have enhanced the reliability and functionality of RFID systems.
Standardization:
The establishment of global standards for RFID technology has facilitated its widespread adoption across various industries, including retail.
Key Drivers for RFID Adoption in Retail
Inventory Accuracy and Efficiency
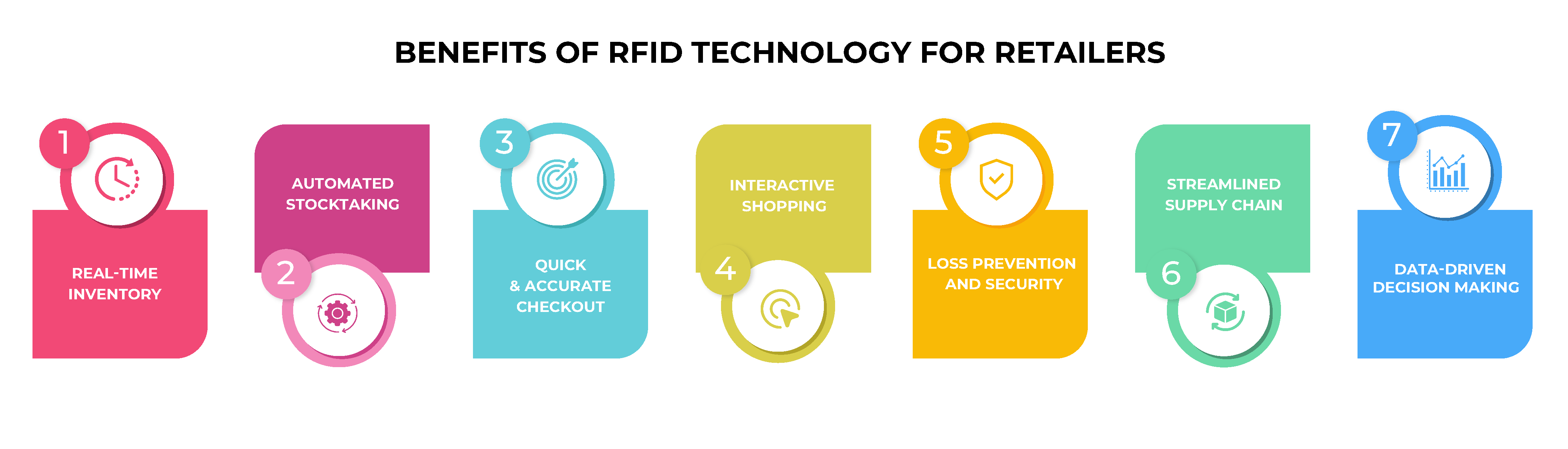
Real-Time Inventory Tracking:
RFID provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, enabling retailers to monitor stock with high accuracy. This reduces the incidence of out-of-stock and overstock situations.
Automated Stocktaking:
Traditional manual inventory counts are time-consuming and prone to errors. RFID automates this process, significantly improving accuracy and reducing labor costs. Enhanced Customer Experience
Quick and Accurate Checkout:
RFID allows for faster checkout processes as items can be scanned en masse rather than individually. This reduces waiting times and improves the overall shopping experience.
Interactive Shopping:
RFID tags can be integrated with interactive displays, providing customers with detailed product information and personalized recommendations.
Loss Prevention and Security
Theft Reduction:
RFID can deter theft by providing real-time alerts when an item leaves the store without being properly checked out.
Supply Chain Security:
RFID enhances the traceability of products throughout the supply chain, reducing the risk of counterfeit goods and ensuring product authenticity. Operational Efficiency
Streamlined Supply Chain:
RFID facilitates better coordination between different stages of the supply chain, from manufacturing to retail. This ensures timely restocking and reduces lead times.
Labor Optimization:
By automating various processes, RFID frees up staff to focus on customer service and other high-value tasks.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Detailed Analytics: RFID systems generate a wealth of data that can be analyzed to gain insights into customer behavior, sales trends, and inventory performance. Dynamic Pricing and Promotions: Retailers can use RFID data to implement dynamic pricing strategies and personalized promotions, enhancing sales and customer loyalty.
Despite its numerous benefits, the implementation of RFID in retail comes with its own set of challenges:
Initial Investment: The upfront cost of RFID systems, including tags, readers, and integration with existing IT infrastructure, can be substantial.
Data Privacy: The use of RFID raises concerns about consumer privacy, as the technology can potentially track customer movements and behavior.
Technical Issues: RFID systems can face technical challenges such as interference from other electronic devices and the need for regular maintenance.
Different types of Retailers are using RFID Retail
1. Apparel and Fashion
Clothing Stores: Major clothing retailers use an RFID retail system to manage large inventories, track items from warehouse to store, and prevent theft.
Footwear: Shoe retailers use RFID for stock management, ensuring the correct sizes and styles are available.
2. Grocery and Supermarkets
Food Retailers: Supermarkets use RFID to track perishable goods, monitor expiry dates, and manage inventory levels efficiently.
Beverage Stores: RFID helps in tracking bottles and cans, particularly in preventing counterfeit products.
3. Electronics
Consumer Electronics: Stores selling gadgets and electronic appliances use RFID for tracking high-value items and managing returns efficiently.
Mobile Stores: Mobile phone retailers use RFID to track phones and accessories, ensuring accurate inventory.
4. Home Improvement and Furniture
Hardware Stores: Retailers like Home Depot use RFID to track tools, hardware, and building materials.
Furniture Retailers: Stores use RFID to manage large items, track inventory in warehouses, and streamline delivery processes.
5. Pharmaceuticals and Health
Pharmacies: RFID is used to track medicines, ensuring the correct stocking of drugs and monitoring expiration dates.
Health and Beauty: Stores selling cosmetics and health products use RFID to manage inventory and prevent theft.
6. Books and Media
Bookstores: RFID is used to track books, manage inventory, and facilitate easy locating of items within the store.
Music and Video Stores: Retailers use RFID to manage inventory of CDs, DVDs, and other media formats.
7. Sporting Goods
Sports Equipment Stores: Retailers use RFID to manage inventory of sports gear, clothing, and accessories, ensuring popular items are always in stock.
8. Jewelry and Luxury Goods
Jewelry Stores: High-value items are tracked using RFID to prevent theft and manage inventory.
Luxury Goods: RFID is used to authenticate and track expensive products, reducing the risk of counterfeiting.
9. Toys and Hobbies
Toy Stores: Retailers use RFID to manage large inventories of toys and hobby items, ensuring availability during peak seasons.
Hobby Shops: Stores selling model kits, crafts, and collectibles use RFID for precise inventory management.
Benefits Across Industries
Improved Inventory Accuracy:
Across all sectors, RFID helps maintain accurate inventory records.
Enhanced Security:
Reduces theft and loss, particularly important in high-value retail sectors.
Operational Efficiency:
Streamlines operations, from warehouse to store shelves, improving restocking and customer service.
The adoption of RFID technology continues to grow as its benefits become more apparent, and costs decrease, making it an integral part of modern retail inventory management.
Future Trends and Developments
The future of RFID in retail looks promising, with several trends expected to shape its evolution:
Integration with IoT:
The integration of RFID with the Internet of Things (IoT) will enable even more granular tracking and management of inventory, enhancing the efficiency of retail operations.
Advancements in Tag Technology:
Ongoing research into smaller, more durable, and cost-effective RFID tags will further reduce the barriers to adoption.
Enhanced Analytics:
The combination of RFID with advanced analytics and machine learning will provide deeper insights into retail operations, enabling more precise forecasting and decision-making.
Conclusion
RFID technology has emerged as a critical tool for retailers, offering a multitude of benefits ranging from improved inventory management to enhanced customer experiences. While there are challenges to its implementation, the advantages far outweigh the drawbacks, making RFID the go-to technology for modern retail operations. As technology continues to evolve, its role in transforming the retail industry is set to become even more significant.
RFID solutions for retail are transforming inventory management and enhancing customer experiences. As retailers increasingly adopt RFID, they gain real-time visibility and efficiency, ultimately driving sales and improving operational performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is RFID technology?
How does RFID work in retail?
What are the benefits of using RFID in retail?
Enhanced Visibility: Offers real-time visibility of inventory across the supply chain.
Reduced Shrinkage: Deters theft and loss by improving product tracking.
Streamlined Operations: Automates inventory counts, reducing the need for manual checks.
Better Customer Experience: Ensures products are always available and easy to find, improving satisfaction.
How can RFID reduce inventory shrinkage?
Can RFID improve the customer shopping experience?
What types of RFID tags are used in retail?
Active RFID Tags: Have their own power source and can send out signals at regular intervals. They are used for high-value item tracking and real-time location services.
Semi-passive RFID Tags: Have a battery to power the chip but rely on the reader for signal transmission. They are used in applications needing greater read range and reliability.
What are the costs associated with implementing RFID in retail?
Are there any privacy concerns with RFID in retail?
How does RFID compare to barcodes in retail?
Read Multiple Tags Simultaneously: RFID can read multiple items at once without line-of-sight.
Greater Data Capacity: RFID tags can store more information than barcodes.
Durability: RFID tags are more durable and less prone to damage.