Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology has revolutionized numerous industries by enabling the automatic identification and tracking of objects. However, like any wireless technology, RFID systems are susceptible to interference and unwanted signal propagation. This is where RF (Radio Frequency) shielding materials come into play. In this blog, we’ll explore why RF shielding is crucial for RFID projects and how it enhances the performance and reliability of these systems.
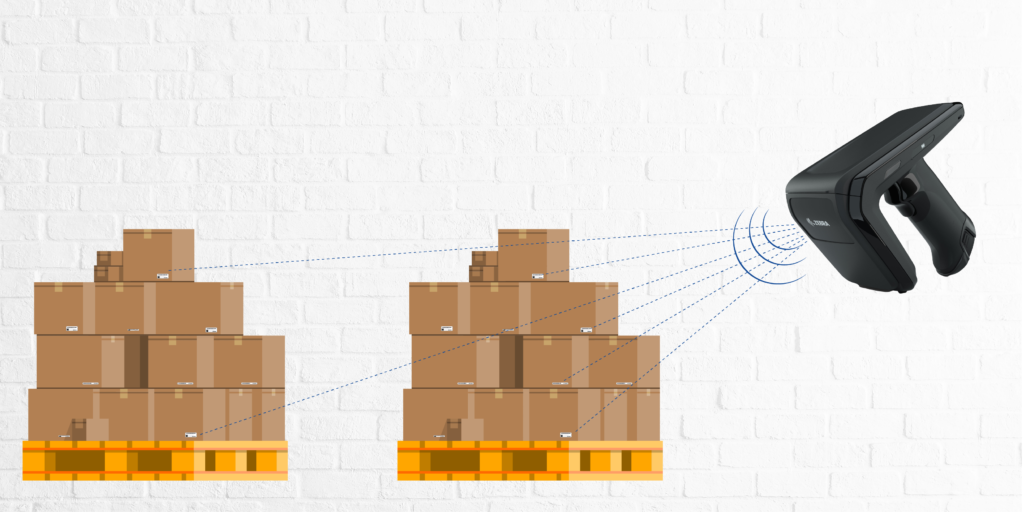
What is RF shielding?
RF shielding involves using materials that block or attenuate radio frequency. These materials are typically conductive, such as metals, and are used to create barriers that prevent RF signals from entering or leaving a particular space. The goal is to control the RF environment within and around RFID systems to ensure optimal performance.
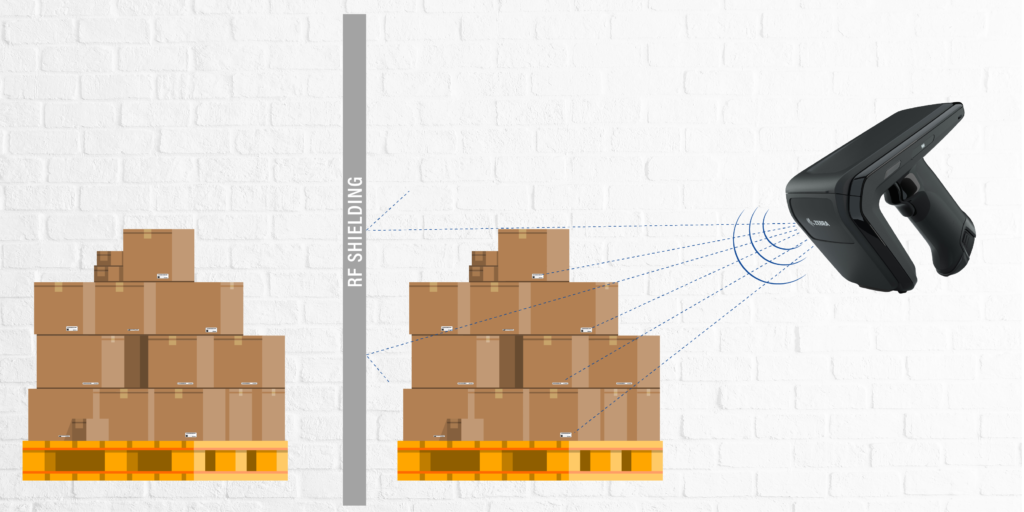
The Importance of RF Shielding in RFID Projects
Reducing Unintended Reads
In certain applications, it is essential to ensure that RFID readers only capture data from specific tags within a defined area. For example, in a retail environment, a reader at the checkout counter should only read items being purchased, not those on nearby shelves. RF shielding materials can be used to create a controlled read zone, preventing unintended RFID tags from being read and ensuring accurate transaction processing.
Preventing Signal Interference
RFID systems operate within specific frequency ranges, commonly in the UHF (860-960 MHz) bands. Other electronic devices, wireless communication systems, and even industrial machinery can emit signals within these ranges, causing interference. This interference can degrade the performance of RFID readers and tags, leading to misreads or failed reads. RF shielding materials help isolate the RFID system from external RF noise, ensuring that only the intended signals are detected and processed.
Improving Read Accuracy and Reliability
In environments with multiple RFID readers and tags, signals can overlap and create a chaotic RF landscape. This phenomenon, known as RF collision or crosstalk, can severely impact read accuracy and system reliability. By strategically placing RF shielding materials, project designers can create isolated zones where RFID readers can operate without interference from neighboring readers. This isolation leads to more accurate and reliable reads, which is crucial in applications like inventory management, asset tracking, and access control.
Enhancing Security
RF shielding also plays a vital role in enhancing the security of RFID systems. Unauthorized access to RFID-tagged assets or information can be a significant concern, especially in sensitive applications such as logistics, healthcare, and government facilities. By using RF shielding materials, project designers can create secure zones where RFID signals are confined, making it difficult for unauthorized individuals to eavesdrop on or interfere with the system. This added layer of security is essential for protecting sensitive data and assets.
Meeting Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory bodies in various countries set limits on the permissible levels of RF emissions to minimize interference with other communication systems and ensure public safety. RFID systems must comply with these regulations, and RF shielding can help achieve compliance by containing the RF signals within the designated operational area. This containment not only ensures regulatory compliance but also prevents potential legal and operational issues.
Common RF Shielding Materials
Several materials are commonly used for RF shielding in RFID projects:
Metal Foils and Sheets: Aluminum, copper, and other metal are widely used due to their high conductivity and ease of installation. These materials can be applied to walls, enclosures, and other surfaces to create effective RF barriers.
Conductive Fabrics: These are flexible materials woven with metal fibers, providing a lightweight and adaptable shielding solution. Conductive fabrics are often used in applications where rigid metal sheets are impractical.
Metalized Coatings and Paints: These coatings can be applied to various surfaces to create a conductive layer that blocks RF signals. They are useful for retrofitting existing structures without extensive modifications.
RF Absorbing Materials: These materials absorb RF energy instead of reflecting it, reducing signal strength and minimizing interference. They are often used in conjunction with reflective shielding to enhance overall performance.
Practical Applications of RF Shielding in RFID Projects
Warehouse and Inventory Management
In large warehouses, multiple RFID readers are used to track inventory items. RF shielding helps create isolated zones where each reader can operate without interference, ensuring accurate inventory counts and efficient asset tracking.
Retail and Point of Sale Systems
In retail environments, RF shielding is used to prevent unintended reads from nearby items, ensuring that only purchased items are scanned at checkout counters. This enhances transaction accuracy and customer satisfaction.
Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
In healthcare settings, RF shielding is crucial for protecting sensitive patient information and ensuring accurate tracking of medical equipment and pharmaceuticals. Shielding also helps prevent interference with other medical devices operating in the same frequency range.
Access Control and Security
RF shielding enhances the security of access control systems by preventing unauthorized reads and ensuring that only authorized personnel can access restricted areas. This is especially important in government buildings, data centers, and high-security facilities.
Here are some use cases demonstrating how RF shielding with Faraday fabric can enhance RFID systems based on the previous case studies:
Use Case: Employing RF Shielding Fabric in Retail to Prevent Unwanted RFID Tag Reads During Inventory
Scenario
A large department store is using RFID technology for efficient inventory management. However, the store is experiencing issues with unintended RFID tag reads during inventory counts, leading to inaccurate stock levels and misplaced items. To address this problem, the store decides to implement RF shielding fabric in specific areas.
Objective
Utilize RF shielding fabric to prevent unwanted RFID tag reads during inventory counts, ensuring accurate inventory levels and reducing the risk of errors.
Implementation
1. Stockroom Segmentation
- Challenge: During inventory counts in the stockroom, RFID readers may pick up tags from nearby sections or even from the sales floor, leading to inaccurate counts.
- Solution: Install RF shielding fabric to create segmented zones within the stockroom. Each zone is shielded to prevent RFID reads from other zones, allowing precise and isolated inventory counts in each section.
2. Sales Floor Control
- Challenge: Inventory counts on the sales floor can be disrupted by tags from adjacent departments or nearby fixtures, causing confusion and errors.
- Solution: Use RF shielding fabric to create designated counting areas on the sales floor. These shielded areas ensure that only the tags within the specific counting zone are read, preventing interference from adjacent departments.
3. Loading Dock Management
- Challenge: RFID tags on newly arrived merchandise at the loading dock can be inadvertently read by inventory readers meant for stockroom or sales floor counts, leading to premature inventory updates.
- Solution: Line the walls and doors of the loading dock with RF shielding fabric. This prevents RFID reads from escaping the loading area, ensuring that new inventory is only scanned and added to the system when it is appropriately placed in the stockroom or sales floor.
4. Display Cases and Fixtures:
- Challenge: Items in display cases or on specific fixtures may be unintentionally read during general inventory counts, leading to duplicated entries or missed items.
- Solution: Incorporate RF shielding fabric into the design of display cases and around particular fixtures. This containment ensures that only the intended items are read during inventory counts, maintaining accurate records.
Use RF shielding fabric to prevent unwanted RFID tag reads on conveyor systems, ensuring accurate tracking and sorting of products as they move through the distribution center.
Choosing the right RF absorber for your application involves several critical considerations to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with your system. Here are the key factors to consider:
Frequency Range
- Compatibility: Ensure the RF absorber is designed to operate effectively within the frequency range of your RFID system.
- Bandwidth: Consider the bandwidth of the absorber to cover all possible frequencies used in your operations.
Material Properties
- Composition: Common materials include ferrite, carbon-loaded foam, and specific polymers. Each material has different absorption properties and suitability for various environments.
- Durability: Choose a material that can withstand the operational environment, including temperature variations, humidity, and physical wear and tear.
Absorption Efficiency
- Attenuation: Check the attenuation levels provided by the absorber. Higher attenuation usually means better absorption but can also affect the signal strength.
- Performance Metrics: Look at parameters such as insertion loss, reflection coefficient, and power handling capability.
Environmental Compatibility
- Temperature and Humidity Resistance: Ensure the absorber material can perform under the temperature and humidity conditions of your application.
- Chemical Resistance: If the conveyor belt is used in an environment with chemicals, choose a material resistant to those substances.
Physical Characteristics
- Size and Thickness: The size and thickness of the absorber should fit the design of your conveyor system without interfering with its operation.
- Flexibility: For conveyor belts that bend or flex, consider materials that are flexible enough to move without breaking or degrading.
Installation and Maintenance
- Ease of Installation: Choose absorbers that are easy to install and do not require extensive modifications to your existing setup.
- Maintenance Requirements: Consider the ease of maintaining the absorbers and their expected lifespan.
Cost and Availability
- Budget: Ensure the RF absorber fits within your budget while meeting the necessary performance criteria.
- Availability: Consider the availability of the material, including lead times for orders and any potential supply chain issues.
Regulatory Compliance
Standards and Certifications: Ensure the RF absorber complies with relevant industry standards and certifications for safety and performance.
Conclusion
RF shielding is a vital component in the design and implementation of RFID projects. By preventing signal interference, improving read accuracy, enhancing security, reducing unintended reads, and ensuring regulatory compliance, RF shielding materials play a crucial role in the success of RFID systems. As RFID technology continues to evolve and find new applications, the importance of effective RF shielding will only grow, making it an essential consideration for project designers and engineers.
