In today’s fast-paced global market, optimizing supply chain efficiency is crucial for businesses aiming to stay competitive. One technology that has significantly transformed supply chain management is Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) pallet tracking. We will explore the impact of RFID pallet tracking on supply chain efficiency, highlighting its benefits, applications, and future potential.
Understanding RFID Technology
RFID technology uses radio waves to identify and track objects. It consists of two main components, RFID tags and RFID readers. RFID tags are small electronic devices that store product information and can be attached to pallets, containers, or individual items. RFID readers use radio waves to communicate with these tags, enabling real-time tracking and data collection.
Benefits of RFID Pallet Tracking
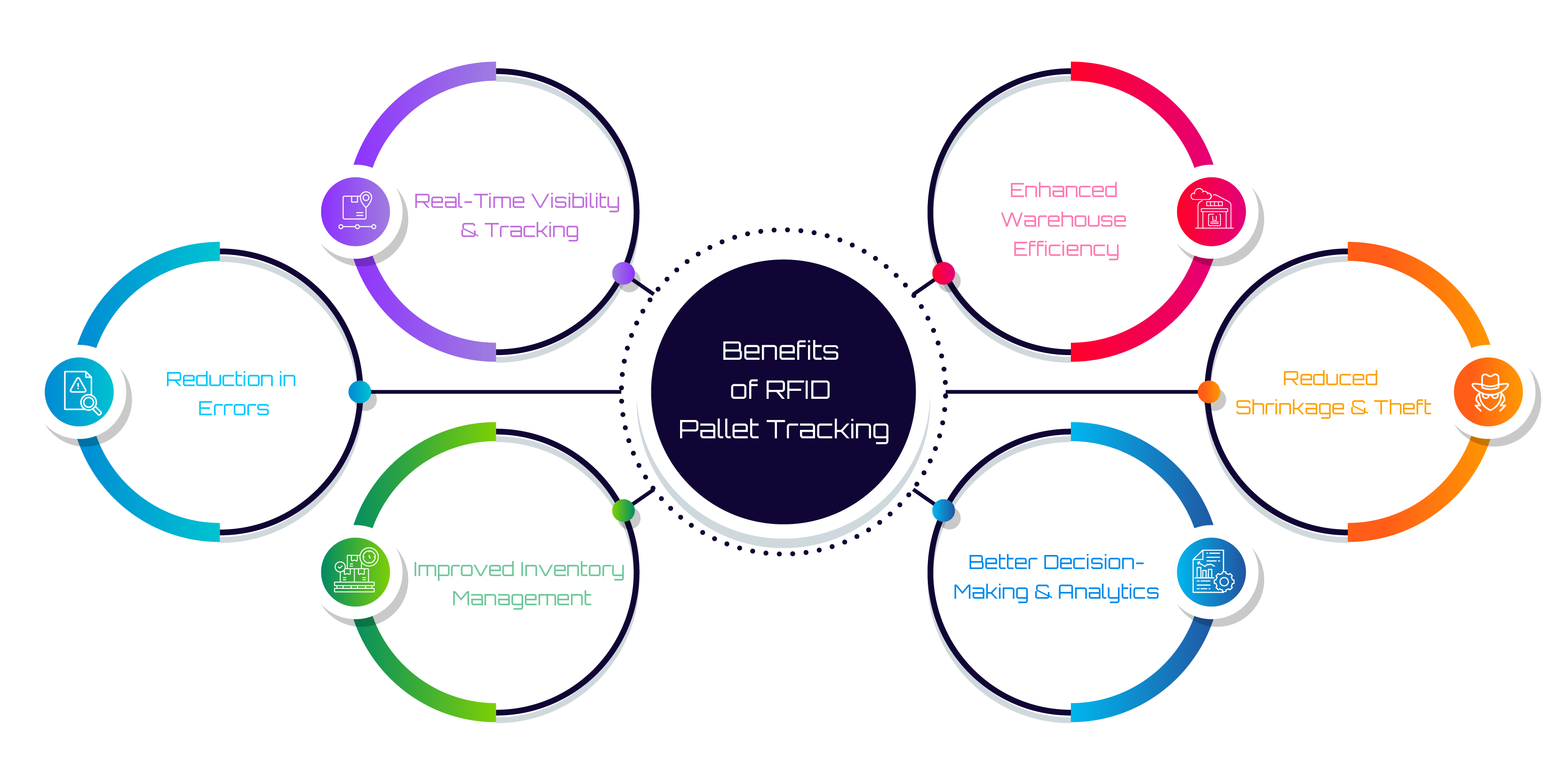
1. Real-Time Visibility and Tracking
RFID provides real-time data on the location and status of pallets as they move through the supply chain. This eliminates manual scanning and delays, enabling businesses to track shipments at various stages, including warehouses, transit, and delivery points.
2. Reduction in Errors
Manual entry errors, misplaced goods, and incorrect shipments are minimized. RFID tags automatically update inventory records, ensuring greater accuracy, which reduces costly mistakes in both inbound and outbound logistics.
3. Improved Inventory Management
With RFID-enabled pallet tracking, businesses can maintain accurate and up-to-date inventory levels. It helps manage stock levels effectively, minimizing both overstock and stockouts, leading to improved inventory turnover.
4. Enhanced Warehouse Efficiency
RFID allows quick identification and location of specific pallets in large warehouses. This speeds up picking, packing, and dispatching processes, reducing labor costs and improving throughput. Automated systems can further streamline pallet movements.
5. Reduced Shrinkage and Theft
RFID systems can track assets throughout the supply chain, reducing shrinkage from theft or misplacement. Alerts can be triggered if pallets leave designated areas, ensuring greater security for goods.
6. Better Decision-Making and Analytics
The data collected from RFID tracking enables more accurate demand forecasting, route optimization, and resource allocation. Businesses can analyze the data to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies, improving overall supply chain performance.
7. Improved Customer Satisfaction
Accurate, real-time information about the status of deliveries leads to better customer service. With RFID, companies can provide precise delivery times and proactively address delays, enhancing customer trust and satisfaction.
8. Automated Compliance and Reporting
RFID can help businesses meet regulatory and contractual requirements by automating the tracking of goods for compliance purposes. It generates reports for auditing and monitoring, making it easier to ensure adherence to standards.
9. Faster Receiving and Shipping Processes
RFID can speed up the receiving and shipping processes by automating data capture. As pallets with RFID tags pass through RFID readers at entry and exit points, the system automatically logs the movement, eliminating the need for manual scanning. This reduces processing time at loading docks and ensures smoother operations.
10. Enhanced Supplier Collaboration
RFID provides better visibility into the supply chain, allowing suppliers and manufacturers to share real-time data. This enhanced collaboration leads to synchronized operations, improved demand forecasting, and better planning for production and inventory management. It also facilitates quick issue resolution, as discrepancies can be identified and addressed immediately.
11. Optimized Transport and Logistics Planning
RFID systems can track pallets in real-time during transit, allowing businesses to monitor shipments’ locations, conditions (e.g., temperature-sensitive goods), and estimated arrival times. This data can be used to optimize transportation routes and schedules, ensuring faster delivery times and lower fuel costs.
12. Reduced Lead Time and Increased Responsiveness
With RFID, companies can respond faster to changes in demand or supply chain disruptions. By having real-time visibility of inventory and pallet movements, businesses can reduce lead times for orders and make swift adjustments to production schedules or shipping routes to meet customer needs.
13. Improved Cross-Docking Operations
In cross-docking, products are unloaded from inbound delivery vehicles and directly loaded onto outbound vehicles without being stored in a warehouse. RFID pallet tracking makes cross-docking more efficient by automating the identification of goods as they arrive and ensuring the correct allocation to outbound shipments, reducing handling time and improving logistics flow.
14. Streamlined Returns and Reverse Logistics
RFID makes managing returns more efficient by tracking pallets and inventory as they come back into the supply chain. RFID tags can help identify which products are being returned, their conditions, and their origin, speeding up the process of restocking, refurbishing, or recycling.
15. Increased Sustainability
By optimizing logistics, reducing unnecessary movements, and enabling better inventory management, RFID can contribute to more sustainable supply chain practices. For example, RFID helps reduce waste due to overproduction, stock obsolescence, and misrouting. This results in a more eco-friendly supply chain with lower carbon footprints.
16. Cost Reduction
Though implementing RFID technology requires initial investment, the long-term benefits can include reduced labor costs, fewer losses due to errors or theft, lower inventory carrying costs, and optimized transportation costs. Over time, these savings can lead to a substantial return on investment (ROI).
17. Increased Asset Utilization
RFID tracking can improve the utilization of assets such as pallets, containers, and other equipment by providing visibility into where and how they are being used. This ensures that assets are deployed more efficiently, reducing downtime and minimizing the need for excess equipment.
Applications of RFID Pallet Tracking
- Warehouse Management: RFID technology streamlines warehouse operations by providing accurate and real-time data on inventory levels. This helps in efficient space utilization, faster order fulfillment, and reduced labor costs.
- Transportation and Logistics: RFID-enabled pallets improve logistics by enabling seamless tracking of goods. Companies can monitor shipment status in real time, optimize delivery routes, and reduce transit times. This ensures timely deliveries and enhances customer satisfaction.
- Retail and Distribution: In retail, RFID technology helps in managing inventory, reducing shrinkage, and improving stock accuracy. It also enhances the customer experience by ensuring product availability and reducing checkout times.
- Manufacturing: RFID tags track raw materials and components throughout the manufacturing process, ensuring timely availability and reducing production delays. This leads to improved production efficiency and reduced downtime.
Advanced Benefits of RFID Pallet Tracking
- Real-Time Data Analytics RFID systems generate vast amounts of data that can be analyzed to gain insights into supply chain operations. Companies can use this data to identify trends, forecast demand, and make informed decisions. Real-time analytics can also help in identifying bottlenecks and optimizing processes.
- Enhanced Customer Experience By ensuring accurate inventory levels and timely deliveries, RFID technology can significantly improve the customer experience. Retailers can provide better service by having the right products available at the right time, reducing wait times, and enhancing overall satisfaction.
- Sustainability and Environmental Impact RFID technology can contribute to sustainability efforts by reducing waste and improving resource utilization. Efficient inventory management means fewer products are discarded due to expiration or obsolescence. Additionally, optimized transportation routes reduce fuel consumption and carbon emissions.
Challenges and Considerations
- Implementation Costs While RFID technology offers numerous benefits, the initial implementation costs can be high. Companies need to invest in RFID tags, readers, and software, as well as train their staff. However, the long-term benefits often outweigh these initial expenses.
- Data Security and Privacy With the increased use of RFID technology, concerns about data security and privacy have emerged. Companies must ensure that their RFID systems are secure and that sensitive information is protected from unauthorized access.
- Integration with Existing Systems Integrating RFID technology with existing supply chain management systems can be challenging. Companies need to ensure compatibility and seamless data flow between different systems to maximize the benefits of RFID.
Case Studies
- Walmart, one of the largest retailers in the world, has successfully implemented RFID technology to improve its supply chain efficiency. By using RFID tags for individual items, Walmart has achieved better inventory accuracy, reduced out-of-stock situations, and improved overall supply chain visibility.
- Amazon uses RFID technology in its warehouses to streamline operations and enhance order fulfillment. RFID tags help in tracking inventory in real-time, reducing the time taken to locate items, and ensuring timely deliveries to customers.
Advanced Applications of RFID Pallet Tracking
- Cold Chain Management In industries like pharmaceuticals and food, maintaining the correct temperature throughout the supply chain is critical. RFID tags equipped with temperature sensors can monitor and record the temperature of pallets in real time. This ensures that products are stored and transported under optimal conditions, reducing spoilage and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
- Automated Replenishment Systems RFID technology can be integrated with automated replenishment systems to streamline inventory management. When inventory levels fall below a certain threshold, the system can automatically trigger reorders, ensuring that stock levels are maintained without manual intervention. This reduces the risk of stockouts and improves overall supply chain efficiency.
- Enhanced Quality Control RFID tags can store detailed information about the production and handling of goods. This data can be used for quality control purposes, allowing companies to trace products back to their origin and identify any issues in the supply chain. This is particularly useful in industries where product recalls are common, such as automotive and electronics.
Real-World Examples
- Zara The fashion retailer Zara has implemented RFID technology across its supply chain to improve inventory management and enhance the customer experience. RFID tags on items allow Zara to track inventory in real-time, ensuring that products are always available in stores and reducing the time taken for stock replenishment.
- Delta Airlines uses RFID technology to track Assets and baggage in real-time. RFID tags on luggage allow Delta to provide passengers with real-time updates on the location of their bags, reducing the incidence of lost luggage and improving customer satisfaction.
Future Innovations
- RFID and Augmented Reality (AR): Combining RFID with AR can provide warehouse workers with real-time information about the location and status of inventory. AR glasses can display information from RFID tags, allowing workers to quickly locate items and streamline warehouse operations.
- RFID and Robots: Autonomous robots equipped with RFID readers can be used to conduct inventory checks in large warehouses or outdoor storage areas. This can significantly reduce the time and labor required for inventory audits, improving accuracy and efficiency.
- RFID in Circular Economy: RFID technology can play a crucial role in the circular economy by tracking products throughout their lifecycle. This enables companies to manage the return, refurbishment, and recycling of products more effectively, reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
Conclusion
Businesses that invest in RFID technology today will be well-positioned to navigate the complexities of the modern supply chain, achieve greater efficiency, and deliver superior value to their customers. The future of supply chain management is undoubtedly bright with the continued adoption and innovation of RFID technology.
RFID pallet tracking is a transformative technology that offers numerous benefits for supply chain management. From improving inventory accuracy and operational efficiency to enhancing customer satisfaction and sustainability, RFID technology has the potential to revolutionize supply chains across various industries. As technology continues to advance, the integration of RFID with other emerging technologies such as IoT, blockchain, and AI will unlock even greater potential for optimizing supply chain operations.