Cities worldwide are becoming smarter, integrating technology to enhance urban living and address challenges like congestion, waste management, and public safety. Among these technologies, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) plays a key role in enabling seamless urban intelligence. This blog explores how RFID is transforming smart cities by providing efficient, real-time solutions.
Smart cities rely on interconnected systems that collect, process, and act on data. RFID technology is a perfect match for such systems due to its ability to track objects, people, and resources accurately. From transportation to healthcare, RFID supports a range of applications that improve urban efficiency and quality of life.
RFID Technology in a Smart City Context
Radio Frequency Identification serves as a cornerstone technology in smart city infrastructure, enabling seamless communication between physical objects and digital systems. The technology utilizes electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to various objects throughout the urban environment. In modern smart cities, RFID systems consist of three primary components: tags that store and transmit data, readers that capture this information, and sophisticated middleware that processes and integrates the collected data into broader city management systems.
Key Advantages of RFID in Urban Applications
Real-Time Data Collection
RFID systems enable instantaneous tracking and monitoring of urban assets, providing city managers with up-to-the-minute information about everything from vehicle movements to utility usage. This real-time capability allows for immediate response to changing conditions and more efficient resource allocation across city services.
Non-Line-of-Sight Operation
Unlike traditional identification methods, RFID technology can function effectively without direct visual contact between the reader and the tag. This capability proves invaluable in urban environments where tags might be obscured by weather conditions, physical barriers, or other obstacles, ensuring consistent operation in challenging city conditions.
Durability and Longevity
RFID tags are engineered to withstand harsh environmental conditions commonly found in urban settings. Their robust construction ensures reliable performance through extreme temperatures, moisture, and physical stress, making them ideal for long-term deployment in outdoor city infrastructure.
Mass Scanning Capabilities
The ability to simultaneously read multiple RFID tags significantly enhances efficiency in urban operations. This feature enables rapid processing of large volumes of tagged items or vehicles, reducing congestion and waiting times in applications like toll collection, parking management, and public transportation.
The Role of RFID in Smart Cities
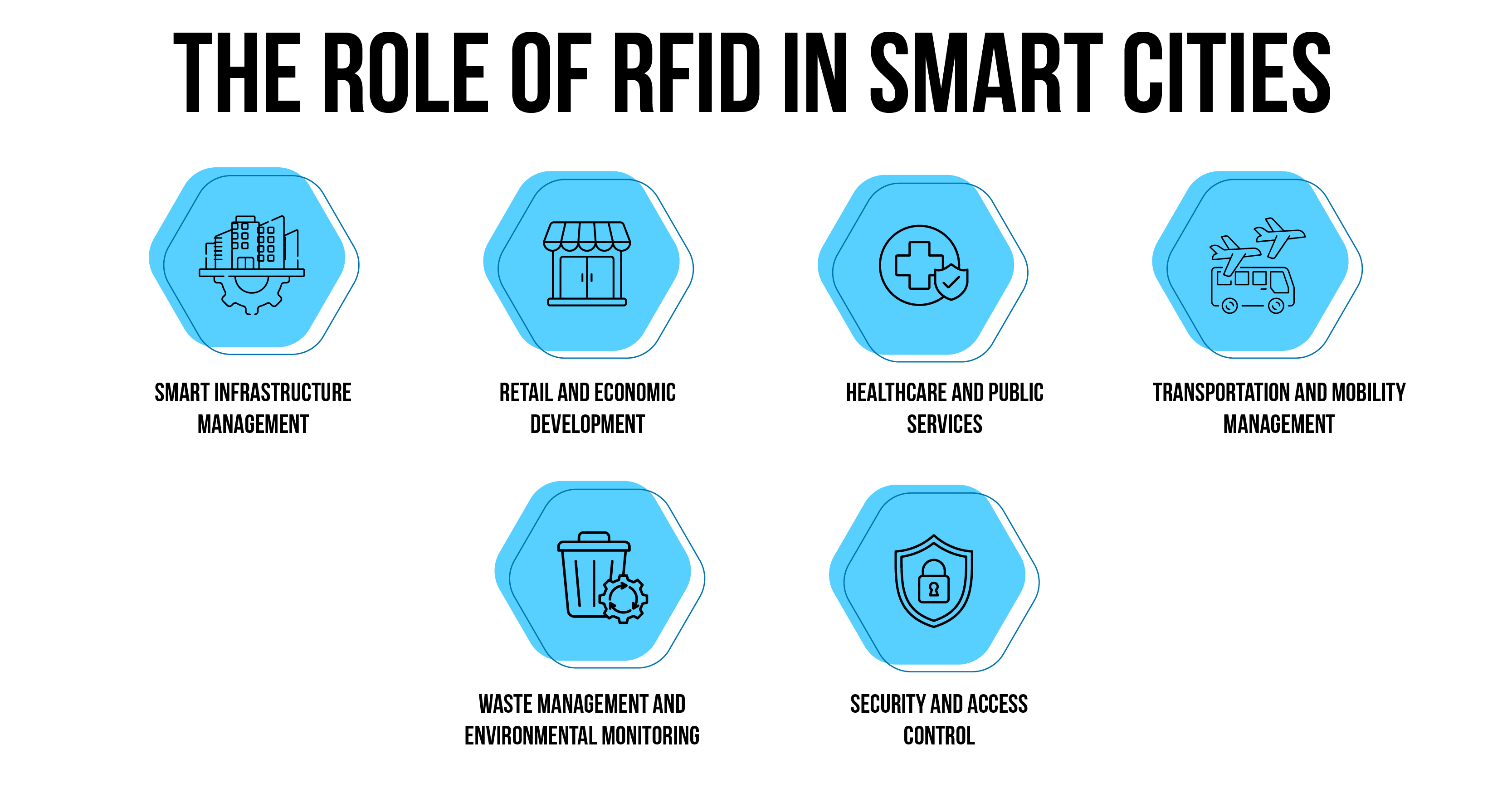
Transportation and Mobility Management
Smart Parking Solutions
Automated Access Control: RFID-equipped gates automatically recognize authorized vehicles, enabling seamless entry and exit while maintaining security. This eliminates manual checks and reduces waiting times at parking facilities.
Real-Time Space Monitoring: RFID sensors embedded in parking spots continuously track occupancy, providing instant updates to drivers through mobile apps and digital displays, significantly reducing time spent searching for spaces.
Dynamic Pricing Systems: Smart RFID systems analyze parking demand patterns to implement variable pricing strategies, optimizing space utilization during peak hours while offering competitive rates during off-peak periods.
Public Transportation
Contactless Payment Systems: RFID-enabled transit cards facilitate quick, secure payments across multiple transportation modes, eliminating the need for cash handling and reducing boarding times.
Fleet Management and Tracking: RFID tags on vehicles enable real-time location tracking, helping operators maintain schedules and respond quickly to service disruptions or emergencies.
Passenger Flow Optimization: RFID monitoring systems analyze passenger volumes and movement patterns, allowing transit authorities to adjust service frequency and capacity based on actual demand.
Traffic Management
Vehicle Identification and Tracking: RFID sensors at key points identify and monitor vehicle movement, enabling automated toll collection and access control while maintaining traffic flow.
Congestion Monitoring: Strategic placement of RFID readers helps track traffic density and flow patterns, providing data for real-time signal adjustments and route recommendations.
Emergency Vehicle Prioritization: RFID-equipped emergency vehicles communicate with traffic signals, automatically adjusting light timing to create clear paths during critical response situations.
Waste Management and Environmental Monitoring
Smart Waste Collection
Bin Fill-Level Monitoring: RFID-integrated sensors continuously measure waste levels in bins, transmitting real-time data to collection centres to optimize pickup schedules and prevent overflow situations.
Route Optimization: Advanced RFID systems analyze bin fill data to generate efficient collection routes, reducing fuel consumption and vehicle wear while ensuring timely waste pickup across the city.
Automated Sorting: RFID tags attached to waste containers enable automatic identification and segregation of different waste types, streamlining recycling processes and improving waste management efficiency.
Environmental Sensing
Air Quality Monitoring: RFID-enabled sensor networks throughout the city measure various pollutants and air quality indicators, providing data for environmental protection initiatives and public health alerts.
Water Management: Smart RFID systems monitor water infrastructure, detecting leaks, tracking usage patterns, and measuring water quality parameters to ensure efficient distribution and maintenance.
Energy Consumption Tracking: RFID sensors integrated with power systems monitor energy usage across different zones, identifying inefficiencies and opportunities for conservation in urban infrastructure.
Security and Access Control
Building Access Management
Residential Complexes and Commercial Buildings: RFID-based access control systems provide secure, contactless entry for residents and employees while maintaining detailed access logs for security purposes.
Government Facilities: High-security RFID authentication systems protect sensitive areas, ensuring only authorized personnel can access restricted zones while tracking all entry and exit activities. The application of RFID in government not only safeguards critical infrastructure but also aids in compliance with security regulations and enhances overall operational efficiency.
Public Safety Applications
Emergency Response Coordination: RFID tracking systems monitor emergency equipment and personnel locations, enabling faster response times and better resource allocation during critical situations.
Crowd Management: RFID sensors analyze foot traffic patterns and crowd density, helping authorities prevent overcrowding and maintain safe conditions in public spaces.
Asset Tracking: Public assets equipped with RFID tags enable real-time monitoring of location and status, preventing theft and ensuring proper maintenance of community resources.
Smart Infrastructure Management
Asset Tracking and Maintenance
Street Lighting Systems: RFID sensors monitor lighting functionality, automatically reporting outages and performance issues to maintenance teams while optimising energy consumption patterns.
Urban Furniture: Smart RFID tags attached to public amenities enable real-time monitoring of condition and location, facilitating quick response to maintenance needs and preventing theft.
Public Utilities: RFID-enabled monitoring systems track the performance and maintenance needs of utility infrastructure, ensuring efficient service delivery and rapid problem resolution.
Infrastructure Monitoring
Bridge and Road Conditions: RFID sensors embedded in infrastructure continuously assess structural health, detecting potential issues before they become serious safety concerns.
Underground Utility Mapping: RFID markers help create precise digital maps of underground infrastructure, preventing accidental damage during excavation and streamlining maintenance operations.
Construction Management: RFID tracking systems monitor equipment, materials, and personnel on construction sites, optimizing resource utilization and improving project efficiency.
Healthcare and Public Services
Hospital Asset Management
Equipment Tracking: RFID systems maintain real-time inventory of medical equipment locations, ensuring critical devices are readily available when needed and preventing loss. The integration of RFID in healthcare enhances efficiency by allowing hospitals to track equipment usage and optimize maintenance schedules.
Patient Identification: Smart RFID wristbands store crucial patient information, reducing identification errors and streamlining care delivery throughout the hospital stay.
Medication Management: RFID-enabled medication tracking ensures accurate dispensing, monitors inventory levels and maintains proper storage conditions for pharmaceuticals.
Emergency Services
Resource Allocation: RFID tracking provides real-time visibility of emergency resources, enabling efficient deployment and management during crisis situations.
Response Time Optimization: Smart RFID systems help emergency teams navigate the fastest routes to incidents, considering traffic conditions and resource availability. The application of RFID in healthcare extends to emergency medical services, where timely interventions can significantly impact patient outcomes.
Personnel Tracking: RFID badges monitor emergency workers’ locations and status, ensuring their safety and enabling better coordination during emergency responses.
Retail and Economic Development
Smart Shopping Experiences
Inventory Management: RFID tags on products provide real-time inventory visibility, automatically triggering restock orders when levels are low and preventing stockouts while optimizing warehouse space. The integration of RFID in retail allows for better inventory control, reducing overhead costs and improving service levels.
Customer Behavior Tracking: Smart RFID systems monitor customer movement patterns and product interactions, providing valuable insights for store layout optimization and merchandising strategies.
Automated Checkout Systems: RFID-powered checkout solutions scan entire shopping carts instantly, eliminating queues and enhancing the customer experience through seamless payment processing.
Supply Chain Optimization
Product Tracking: RFID technology enables continuous monitoring of products throughout the supply chain, ensuring authenticity, preventing losses, and maintaining quality control standards.
Warehouse Management: RFID readers throughout warehouses track item locations and movements, automating inventory counts and improving picking efficiency for faster order processing. The use of RFID in warehouse management streamlines operations, reduces human error, and enhances accuracy in inventory handling.
Last-Mile Delivery: RFID-enabled tracking systems provide accurate delivery status updates, optimize routing, and ensure proper handling of packages during the final delivery phase.
Future Prospects and Innovations
The evolution of RFID technology in smart cities continues to accelerate, driven by groundbreaking innovations in IoT integration, 5G networks, and artificial intelligence. As RFID systems become more sophisticated, they seamlessly connect with vast networks of sensors and devices, leveraging high-speed 5G connectivity and AI-powered analytics. This technological convergence promises to revolutionize urban management, offering unprecedented levels of automation, efficiency, and sustainability in city operations.
Conclusion
RFID technology is a cornerstone of smart city development. By streamlining transportation, waste management, security, and other critical services, RFID enhances urban efficiency and improves the quality of life for residents. As cities continue to evolve, RFID will play an even greater role in shaping a connected and intelligent future.