Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology has been a topic of interest for businesses across various sectors, particularly in retail, supply chain management, healthcare, and manufacturing. The idea of tracking assets, inventory, or products wirelessly seems like a futuristic leap, but is it worth the investment? This comprehensive guide will walk you through the key factors to consider when calculating the Return on Investment (ROI) for RFID technology in your business.
Understanding RFID technology
RFID is a type of wireless communication that uses electromagnetic fields to identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags contain electronically stored information and can be read from a distance, even without a direct line of sight. RFID systems generally consist of three components:
Tags (transponders): RFID tags can be passive (powered by the RFID reader) or active (equipped with their power source).
RFID Readers (interrogators): These devices emit signals to communicate with the RFID tags and retrieve the stored data.
Software: This component processes the data collected by the RFID readers, providing valuable insights for inventory management, asset tracking, or other applications.
Cost Components of RFID Implementation
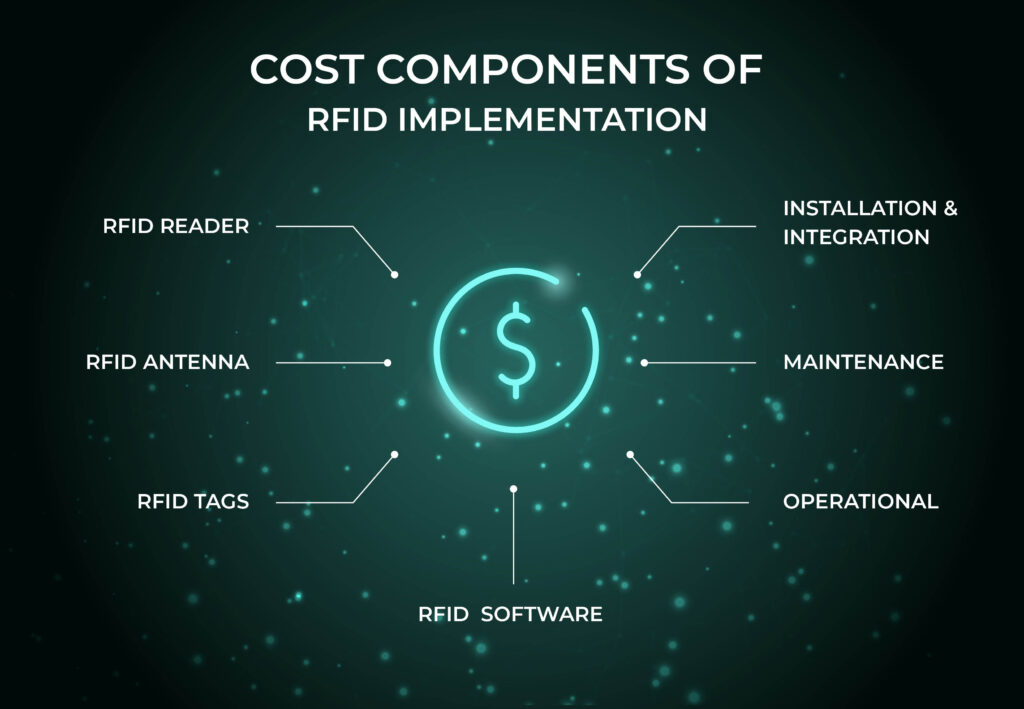
Before diving into the ROI calculation, it’s essential to understand the costs associated with implementing RFID technology:
Hardware Costs: This includes RFID tags, RFID readers, RFID antennas, and any other necessary equipment. Costs vary depending on the type of tags (passive vs. active), the number of readers, and the range of coverage needed.
Software Costs: The software component can include license fees, customization, and integration with existing systems like ERP or inventory management software. Additionally, RFID4U offers TagMatiks AT, TagMatiks AT Lite, TagMatiks Wedge, TagMatiks Retail.
Installation and Integration Costs: Depending on the system’s complexity and the environment, installation can be a significant cost factor. Integration with the existing IT infrastructure and employee training should also be considered.
Maintenance Costs: Ongoing maintenance, such as software updates, hardware replacements, and system support, is another ongoing cost.
Operational Costs: This includes the labor of maintaining the system and managing the generated data.
Benefits of RFID Technology
The primary benefits of RFID technology are rooted in improved efficiency, accuracy, and visibility. Here’s how RFID can impact your business:
Inventory Accuracy: RFID can dramatically reduce human errors in inventory management, leading to near-perfect inventory accuracy.
Increased Efficiency: By automating data collection and reducing manual processes, RFID systems can significantly speed up operations, from inventory checks to asset tracking.
Enhanced Visibility with RFID: With real-time data, businesses can achieve better visibility into their supply chains, leading to faster decision-making and improved responsiveness.
Loss Prevention with RFID: RFID can help in reducing theft, loss, and misplaced items, contributing to a decrease in shrinkage.
Improved Customer Experience: With accurate inventory data, businesses can ensure product availability, reduce out-of-stock, and provide better service to customers.
Calculating ROI for RFID
Calculating the ROI for RFID involves comparing the total cost of ownership (TCO) against the financial gains resulting from the technology’s deployment. Here’s a step-by-step approach
Step 1: Define the Objectives
Clearly define what you hope to achieve with RFID. Common objectives might include:
- Reducing inventory shrinkage
- Improving inventory accuracy
- Increasing operational efficiency
- Enhancing the customer experience
Step 2: Quantify the Benefits
Once objectives are defined, quantify the potential benefits. This involves:
Reduced Labor Costs: Calculate the savings from reduced manual inventory counts and asset tracking.
Decreased Shrinkage of Items: Estimate the loss reduction due to theft or misplaced items.
Increased Sales: Consider the potential increase in sales due to better inventory visibility and product availability. It is always subject to the type of business you have.
Reduced Stockouts and Overstocks: Quantify the financial impact of having the right amount of inventory at the right time.
Step 3: Assess the costs.
List all the costs associated with the RFID implementation.
Initial Costs: Include the costs of RFID tags, RFID readers, RFID antennas, and RFID software.
Ongoing Costs: Consider maintenance, RFID software updates, and the labor required to manage the system.
Integration Costs: Factor in integrating RFID with your current systems.
Step 4: Calculate the ROI.
Use the following formula to calculate the ROI:
Return on investment :
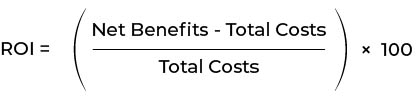
Net benefits are the total financial gains from RFID implementation (e.g., cost savings, and increased revenue). Total costs include both the initial and ongoing costs of the RFID system.
Step 5: Consider the Payback Period
The payback period is the time it takes for the investment to pay for itself. It’s calculated by dividing the initial costs by the annual net benefits. A shorter payback period generally indicates a better investment.
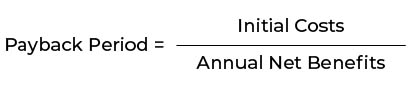
Different Industry-Specific ROI Considerations:
ROI Considerations
Different industries may experience varying levels of ROI based on their unique use cases for RFID. Here’s a look at how RFID ROI might differ across sectors:
Retail :
In RFID retail, RFID is primarily used for inventory management, loss prevention, and enhancing the customer experience. Increased sales often drive the ROI due to better stock management and reduced shrinkage.
Example: A retail chain implemented RFID and saw a 10% increase in sales due to improved inventory accuracy and a 20% reduction in shrinkage.
Healthcare :
RFID in healthcare is used for tracking equipment, managing inventory, and ensuring patient safety. The ROI might come from reduced equipment losses, better inventory control, and improved patient care.
Example: A hospital reduced the loss of expensive medical equipment by 15% after implementing RFID, leading to significant cost savings.
Manufacturing :
RFID in manufacturing can streamline production processes, improve asset tracking, and enhance quality control. The ROI often comes from increased operational efficiency and reduced downtime.
Example: A manufacturing plant reduced downtime by 25% through RFID-enabled asset tracking, resulting in a significant boost to productivity.
Supply Chain and Logistics :
RFID is valuable in supply chain and logistics for tracking shipments, reducing errors, and improving supply chain visibility. The ROI often comes from reduced labor costs, fewer shipping errors, and better inventory management.
Example: A logistics company reduced shipping errors by 30% after implementing RFID, leading to fewer returns and increased customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the key to a successful RFID implementation lies in careful planning, realistic expectations, and a clear understanding of both the technology and your business needs. If done correctly, RFID can offer a substantial ROI, making it a valuable investment in the long-term success of your business.
RFID is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and its value will depend on your specific industry, use case, and business goals. For some, the benefits may far outweigh the costs, leading to substantial long-term gains. For others, the investment might be too high, or the benefits too uncertain, to justify the expense.
Investing in RFID technology can be a game-changer for many businesses, offering significant improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and visibility. However, the decision to invest should be based on a thorough analysis of costs, benefits, and potential ROI. By carefully considering your objectives, quantifying the benefits, and assessing the costs, you can determine whether RFID is worth the investment for your business.
