
NFC is a set of short-range wireless technologies that usually function over a distance of around 2 to 4 centimeters (1-2 inches) or less. NFC technology, which is part of the Radio Frequency Identification or RFID technology operates at 13.56 MHz on ISO/IEC 18000-3 air interface and at rates ranging from 106 kbit/s to 424 kbit/s. It works just like any high frequency RFID as it uses inductive coupling (utilizing magnetic induction) where the antenna of one device (reader or an initiator) generates a magnetic that then subsequently powers the second device or a target that has embedded NFC tag. This enables NFC targets to take very simple form factors such as tags, stickers, key fobs, or cards that do not require batteries. For more information on how inductive coupling works, check out Inductive versus Capacitive Coupling. However, because the target device is often more complex and includes a battery, a smart phone for instance, the NFC technology allows the initiator and target to switch places.
NFC devices are unique in that they can change their mode of operation to be in reader/writer mode, peer-to-peer mode, or card emulation mode. The different operating modes are based on the ISO/IEC 18092 NFC IP-1 and ISO/IEC 14443 contactless smart card standards.
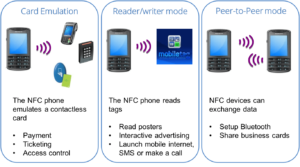
In the Card Emulation Mode, the NFC device works just like a regular (passive RFID) smart card. Because of this, the NFC enabled mobile phones can be used for contactless payments, ticketing and access control and a lot of the existing infrastructure and processes can be reused. In this mode, the devices do not have to be powered as the card emulation does not require support from the processor/OS and will, if enabled, work when when the phone is out of battery.
In the Reader/Writer Mode, the NFC device is capable of reading NFC tags. The tag can contain various data, including a message or URL. This option can be utilized for advertising, much the same as 2-D barcodes. Poster or flyer can be scanned by an NFC phone and the customer is then taken to a website, advertisement, coupon or alike.
In the Peer to Peer Mode, two NFC devices can exchange data. For example, it can be used for setting up a Bluetooth connection by just tapping the devices. It can also be used for exchanging content like virtual business cards and digital photos.
In the next post we will explore the security of NFC devices!